AI hallucinations are derailing enterprise deployments across industries. A single fabricated answer in healthcare, finance, or legal applications can trigger compliance violations and erode customer trust. Learning how to reduce AI hallucinations has become essential for organizations deploying large language models in production environments.
Moreover, these errors often emerge after months of development work, forcing teams to rebuild validation layers from scratch. Therefore, this guide explores proven techniques that engineering teams use to reduce AI hallucinations and build reliable, accurate AI systems.
Why AI Hallucinations Occur in LLMs
Large language models operate as probability engines. They predict the next most likely token based on training patterns, not a verified knowledge database. Consequently, when faced with ambiguous prompts or outdated information, they generate plausible-sounding text rather than admitting uncertainty.
Common triggers include incomplete context, vague questions, and requests about events after the model’s knowledge cutoff. Additionally, models sometimes overfit to training patterns and produce outputs that sound authoritative but lack factual grounding.

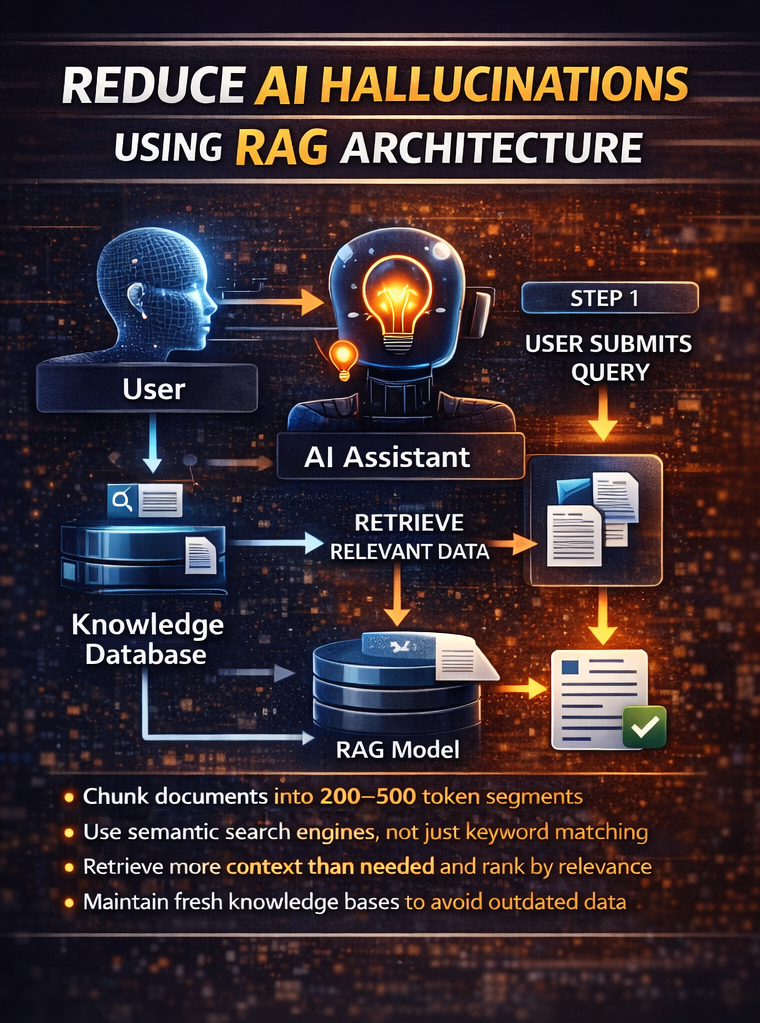
Reduce AI Hallucinations Using RAG Architecture
Retrieval Augmented Generation has emerged as the primary method to reduce AI hallucinations in production systems. Instead of relying solely on parametric knowledge, RAG systems inject relevant context directly into each prompt. As a result, the model grounds its responses in your actual documentation and verified sources.
The architecture works through four steps. First, a user submits a query. Second, the system retrieves relevant documents from your knowledge base. Third, retrieved context gets added to the prompt. Finally, the LLM generates a response anchored in that specific information.
RAG Implementation Best Practices
- Chunk documents into 200-500 token segments for optimal retrieval
- Use semantic search engines instead of keyword matching alone
- Retrieve more context than needed and rank by relevance
- Test embedding models on domain-specific queries before deployment
- Maintain fresh knowledge bases to avoid grounding answers in outdated data
A customer support system without RAG might invent product features. In contrast, the same system with proper retrieval pulls from actual specifications and support documentation. Furthermore, teams report accuracy improvements of 40-60 percent after implementing RAG correctly to reduce AI hallucinations.
Prompt Engineering Strategies to Reduce Hallucinations
Prompt design has a measurable impact on output accuracy. Similarly, small structural changes can reduce error rates without modifying the underlying model. For example, explicitly instructing models to acknowledge uncertainty prevents confident fabrication and helps reduce AI hallucinations significantly.
Effective Prompt Structures
Be explicit about limitations. Instead of generic instructions, specify: “Answer using only the provided context. If the context is insufficient, state that you don’t have enough information.” This simple change forces models to recognize knowledge gaps.
Constrain output formats. JSON schemas, bullet lists, and fill-in-the-blank templates limit the model’s ability to improvise. Therefore, structured outputs work particularly well for factual extraction tasks.
Implement multi-step verification. Ask the model to identify relevant facts first, then construct an answer, then verify claims against source material. Consequently, this approach catches inconsistencies before they reach users.
Include quality examples. Showing 2-3 examples of correct responses with proper citations improves consistency. In fact, one legal technology company reduced hallucinations by 60 percent through prompt restructuring alone.
Fine-Tuning Models to Reduce AI Hallucinations
Fine-tuning improves accuracy in narrow domains where you possess high-quality training data. However, it requires thousands of examples and works best for specialized terminology and consistent formatting needs. Moreover, combining fine-tuning with RAG and validation layers delivers better results than any single technique when you want to reduce AI hallucinations.
Consider fine-tuning when your field uses terminology that differs from general web text. Additionally, it helps when you need consistent tone or handle well-defined use cases. Conversely, avoid fine-tuning if your domain changes frequently or you have limited training examples.
Validation Layers That Reduce AI Hallucinations
Production systems need guardrails beyond the LLM itself. Therefore, implementing confidence scoring and validation mechanisms prevents errors from reaching end users. Furthermore, these layers provide measurable quality metrics for ongoing improvement and help reduce AI hallucinations effectively.
Confidence Scoring Methods
- Ask models to rate their own certainty levels
- Generate multiple outputs and measure consistency
- Calculate semantic similarity between responses and source documents
- Flag hedge language like “might,” “possibly,” or “it’s likely”
Practical Validation Approaches
- Route critical outputs through a secondary fact-checking model
- Apply rule-based validation for structured data like dates and IDs
- Implement human review for high-stakes decisions
- Log and audit low-confidence outputs weekly
A healthcare AI platform built a validation system that flags any medical claim without direct source attribution. As a result, the added 200ms latency eliminated an entire class of liability risk. Similarly, financial services firms use dual-model verification for regulatory compliance.
Model Selection Strategies
Different models hallucinate at different rates. Newer generations like Claude Sonnet 4, GPT-4, and Gemini 1.5 Pro demonstrate measurably better factual accuracy than earlier versions. However, smaller specialized models often outperform larger general-purpose ones in narrow domains when teams need to reduce AI hallucinations.
Benchmark candidates on your specific use case rather than relying on public leaderboards. Additionally, test with adversarial queries designed to trigger errors. Measure both accuracy and appropriate refusal rates, as saying “I don’t know” is often the correct response.
Some production systems use multiple models strategically. For instance, a fast small model handles straightforward queries while a more capable model processes complex or ambiguous requests. Consequently, this approach balances latency, cost, and accuracy requirements.
Continuous Monitoring to Reduce Hallucinations
Hallucination patterns evolve as systems scale and users ask unexpected questions. Therefore, establishing feedback loops helps teams identify and address new failure modes quickly. Moreover, regular testing against known-hard queries prevents regression and ensures your efforts to reduce AI hallucinations remain effective.
Essential Monitoring Metrics
- Track user corrections and negative feedback signals
- Log queries where models expressed low confidence
- Monitor factual errors in production outputs
- A/B test prompt variations and architecture changes
- Review citation quality and source attribution rates
Create a golden test set of queries that previously triggered hallucinations. Run your system against this benchmark weekly to detect performance degradation. Furthermore, one B2B platform built dashboards tracking hedge language frequency and user correction rates, investigating immediately when metrics cross predefined thresholds.
According to NIST’s AI framework, continuous validation and monitoring form essential components of trustworthy AI systems in production environments.
Combining Techniques to Reduce AI Hallucinations
The most effective approach to reduce AI hallucinations involves layering multiple strategies. Successful production systems typically combine RAG for data grounding, prompt engineering for clear instructions, fine-tuning when domain data exists, validation layers to catch errors, and continuous monitoring to detect new issues.
A legal research platform implemented all five techniques. Their pipeline retrieves relevant case law, uses structured prompts requiring citations, fine-tunes on legal documents, validates outputs against sources, and tracks accuracy metrics. As a result, hallucination rates dropped from 23 percent to under 3 percent.
Similarly, financial advisory systems combine regulatory document retrieval with multi-step verification. Therefore, they maintain compliance while delivering accurate guidance to advisors and clients.
When Perfect Accuracy Isn’t Achievable
Some use cases demand zero tolerance for errors. Medical diagnosis, legal advice, and financial reporting require certainty that current LLMs cannot guarantee. Consequently, teams must evaluate whether generative AI is appropriate for their specific application and whether they can adequately reduce AI hallucinations to acceptable levels.
Alternative approaches include hybrid systems where LLMs draft content and humans verify, constrained generation from structured databases, deterministic rules engines for high-stakes decisions, and using LLMs for discovery rather than final answers. Moreover, being transparent about limitations builds more trust than deploying unreliable systems.
Building Production-Ready AI Systems
Reducing hallucinations requires ongoing discipline across architecture, evaluation, and operations. Start with RAG and prompt engineering for immediate improvements. Additionally, layer in validation, monitoring, and specialized models as you scale.
Most importantly, measure everything systematically. You cannot improve what you do not track. Therefore, establish baselines, set thresholds, and review performance metrics regularly to ensure your strategies to reduce AI hallucinations continue working effectively.
At AiBridze, we help organizations design and deploy AI solutions that balance innovation with reliability. Our team works with companies building production LLM systems in regulated industries, ensuring accuracy and compliance from architecture through deployment. If you’re ready to explore how to reduce AI hallucinations in your specific context, reach out to discuss your requirements.






